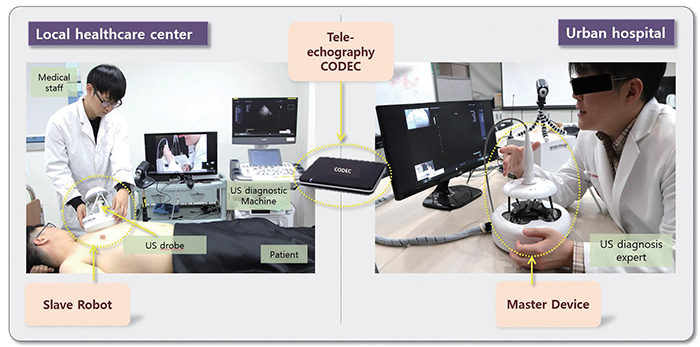
Robot-assisted tele-echography system based on slave-master
robots integrated with ICT that allows elderly patients living in remote
areas to receive advanced medical services such as ultrasound
imaging without having to travel long distances to urban hospitals.
When the ultrasound diagnostic specialist in the urban hospital
manipulates the probe model of the master device, the remotely
controlled slave robot mimics the diagnostic motion to obtain
ultrasonic images in real-time.
The system consists of 1) ‘Slave robot’ that will be applied on the
patient, 2) ‘Master device’ that the specialist will manipulate, and
3) ‘Tele-echography CODEC’ that will connect slave and master
systems though the broadband internet.
Client / Market
- Remotely controlled ultrasonic diagnosis by an ultrasound specialist for people
living in remote areas, military camps, deep-sea fishing vessels with limited access
to medical benefit, aged patients who can’t travel far distance, emergency patients,
and patients in affected areas
Necessity of this Technology
- Currently, a remotely controlled medical system is being provided for patients with
limited medical benefits like those in remote areas, military camps, and deepsea
fishing vessels, but mostly it is offered through online counseling or medical
examination by audio-visual interview. Diseases and body parts that could be
handled remotely area are very limited.
- Ultrasonic image diagnosis is noninvasive, harmless to human, and simple. Because
the cross-sectional anatomic image can be acquired in real-time, it can diagnose
various diseases and body parts. However, depending on the diagnostic area, there
is a specialist, and only experienced and trained ultrasound specialists can read the
acquired ultrasound image.
- Recently, ultrasonic diagnostic equipment has become smaller for convenient
mobility, but realistically, there is a limit regarding dispatching ultrasound
specialists to medically isolated areas.
Technical Differentiation
- Previously, tele-echography systems have been introduced in France and Japan,
however the new system is light-weighted (1.2 kg) compared to the existing
diagnostic robots and is small enough to carry with one hand. It allows more
versatile diagnostic motion (6 DOF + 1 rotation axis) and enables more convenient
remotely controlled ultrasonic diagnosis

Excellence of Technology
- The robot can be easily connected to existing ultrasonic imaging device, is light (1.2 kg)
and small to be conveniently carried to the medically isolated areas and able to copy
the probe movement mimic the motion of ultrasound diagnosis in all directions (6 DOF
+ 1 rotation axis).
- Maximum pressing force of 5 Kgf; can handle over 1Hz-speed of motion for general
ultrasonic diagnosis by specialists
- Upgraded form compared to a commercialized product (Company A of France) with
a similar concept (hand-held) which is heavy (3.5 kg) and requires a cradle and has
less DOF for movement (4 DOF)
- To minimize operating error that may occur while remotely controlling of the robot
movement, a master device with the same structure as the slave was developed for
intuitive control.
- Even in remote areas with poor internet connection, the wireless LTE network used
for mobile phones can be used to connect to the master site to enable robot control.
CURRENT INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT STATUS
PATENT
- Remotely Controlled Echography System (KR2017-0106527, US14/966,823), Remotely Controlled Apparatus for Echography
KNOW-HOW
- Robot design technology that can move the ultrasonic probe in 6 degree of freedom while light-weight(1.2 Kg), Hand-held type,
pressing force of 5 Kgf.
- Master device design optimized for tele-echography by enabling intuitive remote motion control of slave robot.
- Hardware CODEC technology for transparent robot control and ultrasonic Image transmission in internet/mobile environment
- Technology for real-time remote robot control
|






